AWS supports identity federation using SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) 2.0. Using SAML, you can configure your AWS accounts to integrate with your identity provider (IdP). Once configured, your federated users are authenticated and authorized by your organization’s IdP, and then can use single sign-on (SSO) to sign in to the AWS Management Console. This not only obviates the need for your users to remember yet another user name and password, but it also streamlines identity management for your administrators. This is great if your federated users want to access the AWS Management Console, but what if they want to use the AWS CLI or programmatically call AWS APIs?
On the AWS blogs and forums there are some posts about a Python2 and Python3 script were the latest version I could find seems to be located here. We needed a few tweaks to the script so for future reference and sharing here is the version we use.
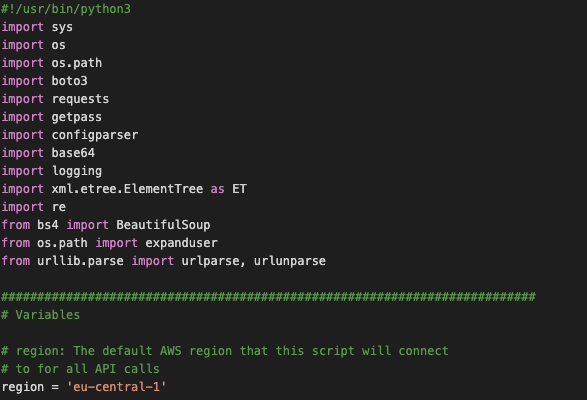
#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
import os
import os.path
import boto3
import requests
import getpass
import configparser
import base64
import logging
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from os.path import expanduser
from urllib.parse import urlparse, urlunparse
##########################################################################
# Variables
# region: The default AWS region that this script will connect
# to for all API calls
region = 'eu-west-1'
# output format: The AWS CLI output format that will be configured in the
# saml profile (affects subsequent CLI calls)
outputformat = 'json'
# awsconfigfile: The file where this script will store the temp
# credentials under the saml profile
awsconfigfile = '/.aws/credentials'
# SSL certificate verification: Whether or not strict certificate
# verification is done, False should only be used for dev/test
sslverification = True
# idpentryurl: The initial url that starts the authentication process.
idpentryurl = 'https://ilionx.tmpldesign.nl/adfs/ls/IdpInitiatedSignOn.aspx?loginToRp=urn:amazon:webservices'
# Uncomment to enable low level debugging
#logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
##########################################################################
# Write the AWS STS token into the AWS credential file
home = expanduser("~")
filename = home + awsconfigfile
# used only for the conditions to check .aws folder exists or not
directory = '.aws'
awsconfig = os.path.join(home, directory)
# Condition to check the ~/.aws/config and ~/.aws/credentails files
# AWS Credentails file
print ('CHECKING THE AWS CREDENTAILS FILE EXISTS OR NOT')
if os.path.exists(filename) and os.path.isfile(filename):
print("aws credentails file exists")
else:
if (not os.path.exists(awsconfig)) and (not os.path.isdir(awsconfig)):
os.mkdir(awsconfig)
# Create an empty file.
# Open a file with writing mode, and then just close it.
print("FILE NOT EXISTS, CREATING CREDENTAILS FILE")
with open(os.path.join(awsconfig, 'credentials'), 'w') as f:
f.write("[default]n")
f.write("aws_access_key_id = dummyn")
f.write("aws_secret_access_key = dummy123n")
print("CREDENTAILS FILE CREATED")
# AWS config file
print ('CHECKING THE AWS CONFIG FILE EXISTS OR NOT')
config_file = '/.aws/config'
confilg_file_name = home + config_file
if os.path.exists(confilg_file_name) and os.path.isfile(confilg_file_name):
print("aws config file exists")
else:
print("FILE NOT EXISTS, CREATING CONFIG FILE")
# Create an empty file.
# Open a file with writing mode, and then just close it.
with open(os.path.join(awsconfig, 'config'), 'w') as f:
f.write("[default]n")
f.write("region = eu-central-1n")
f.write("output = jsonn")
print("CONFIG FILE CREATED")
# Get the federated credentials from the user
print("Username:", end=' ')
username = input()
password = getpass.getpass()
print('')
# Initiate session handler
session = requests.Session()
# Programmatically get the SAML assertion
# Opens the initial IdP url and follows all of the HTTP302 redirects, and
# gets the resulting login page
formresponse = session.get(idpentryurl, verify=sslverification)
# Capture the idpauthformsubmiturl, which is the final url after all the 302s
idpauthformsubmiturl = formresponse.url
# Parse the response and extract all the necessary values
# in order to build a dictionary of all of the form values the IdP expects
formsoup = BeautifulSoup(formresponse.text)
payload = {}
for inputtag in formsoup.find_all(re.compile('(INPUT|input)')):
name = inputtag.get('name','')
value = inputtag.get('value','')
if "user" in name.lower():
#Make an educated guess that this is the right field for the username
payload[name] = username
elif "email" in name.lower():
#Some IdPs also label the username field as 'email'
payload[name] = username
elif "pass" in name.lower():
#Make an educated guess that this is the right field for the password
payload[name] = password
else:
#Simply populate the parameter with the existing value (picks up hidden fields in the login form)
payload[name] = value
# Debug the parameter payload if needed
# Use with caution since this will print sensitive output to the screen
#print payload
# Some IdPs don't explicitly set a form action, but if one is set we should
# build the idpauthformsubmiturl by combining the scheme and hostname
# from the entry url with the form action target
# If the action tag doesn't exist, we just stick with the
# idpauthformsubmiturl above
for inputtag in formsoup.find_all(re.compile('(FORM|form)')):
action = inputtag.get('action')
loginid = inputtag.get('id')
if (action and loginid == "loginForm"):
parsedurl = urlparse(idpentryurl)
idpauthformsubmiturl = parsedurl.scheme + "://" + parsedurl.netloc + action
# Performs the submission of the IdP login form with the above post data
response = session.post(
idpauthformsubmiturl, data=payload, verify=sslverification)
# Debug the response if needed
#print (response.text)
# Overwrite and delete the credential variables, just for safety
username = '##############################################'
password = '##############################################'
del username
del password
# Decode the response and extract the SAML assertion
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text)
assertion = ''
# Look for the SAMLResponse attribute of the input tag (determined by
# analyzing the debug print lines above)
for inputtag in soup.find_all('input'):
if(inputtag.get('name') == 'SAMLResponse'):
#print(inputtag.get('value'))
assertion = inputtag.get('value')
# Better error handling is required for production use.
if (assertion == ''):
#TODO: Insert valid error checking/handling
print('Response did not contain a valid SAML assertion')
sys.exit(0)
# Debug only
# print(base64.b64decode(assertion))
# Parse the returned assertion and extract the authorized roles
awsroles = []
root = ET.fromstring(base64.b64decode(assertion))
for saml2attribute in root.iter('{urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion}Attribute'):
if (saml2attribute.get('Name') == 'https://aws.amazon.com/SAML/Attributes/Role'):
for saml2attributevalue in saml2attribute.iter('{urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion}AttributeValue'):
awsroles.append(saml2attributevalue.text)
# Note the format of the attribute value should be role_arn,principal_arn
# but lots of blogs list it as principal_arn,role_arn so let's reverse
# them if needed
for awsrole in awsroles:
chunks = awsrole.split(',')
if'saml-provider' in chunks[0]:
newawsrole = chunks[1] + ',' + chunks[0]
index = awsroles.index(awsrole)
awsroles.insert(index, newawsrole)
awsroles.remove(awsrole)
# If I have more than one role, ask the user which one they want,
# otherwise just proceed
print("")
if len(awsroles) > 1:
i = 0
print("Please choose the role you would like to assume:")
for awsrole in awsroles:
print('[', i, ']: ', awsrole.split(',')[0])
i += 1
print("Selection: ", end=' ')
selectedroleindex = input()
# Basic sanity check of input
if int(selectedroleindex) > (len(awsroles) - 1):
print('You selected an invalid role index, please try again')
sys.exit(0)
role_arn = awsroles[int(selectedroleindex)].split(',')[0]
principal_arn = awsroles[int(selectedroleindex)].split(',')[1]
else:
role_arn = awsroles[0].split(',')[0]
principal_arn = awsroles[0].split(',')[1]
# Use the assertion to get an AWS STS token using Assume Role with SAML
client = boto3.client('sts', region_name = region)
token = client.assume_role_with_saml(
RoleArn=role_arn,
PrincipalArn=principal_arn,
SAMLAssertion=assertion)
# Read in the existing config file
config = configparser.RawConfigParser()
config.read(filename)
# Put the credentials into a saml specific section instead of clobbering
# the default credentials
if not config.has_section('saml'):
config.add_section('saml')
print(token)
config.set('saml', 'output', outputformat)
config.set('saml', 'region', region)
config.set('saml', 'aws_access_key_id', token['Credentials']['AccessKeyId'])
config.set('saml', 'aws_secret_access_key', token['Credentials']['SecretAccessKey'])
config.set('saml', 'aws_session_token', token['Credentials']['SessionToken'])
# Write the updated config file
with open(filename, 'w+') as configfile:
config.write(configfile)
# Give the user some basic info as to what has just happened
print('nn----------------------------------------------------------------')
print('Your new access key pair has been stored in the AWS configuration file {0} under the saml profile.'.format(filename))
print('Note that it will expire at {0}.'.format(token['Credentials']['Expiration']))
print('After this time, you may safely rerun this script to refresh your access key pair.')
print('To use this credential, call the AWS CLI with the --profile option (e.g. aws --profile saml ec2 describe-instances).')
print('----------------------------------------------------------------nn')